EOS, the technology and market leader for design-driven, integrated solutions for additive manufacturing (AM), is exhibiting at the 35th International Dental Show (IDS), the world’s leading fair for the dental industry. During March 12 to 16 EOS is showcasing its dental solutions in Cologne in Hall 4.1, booth F050 and introduces its new removable partial denture (RPD) solution. With the AM technology, laboratories and manufacturing service providers can produce high-quality dental crowns and bridges, plastic dental models and removable partial dentures in a highly productive way and at attractive costs per part. “Currently, an industrialization process is changing the dental industry in a sustained manner. The EOS technology process contributes to an automation and digitalization of manufacturing processes. With AM via laser-sintering, digital technologies have become established in several fields of dentistry and are already a firm part of the industry. Laser-sintered dental prostheses have almost completely replaced precision casting in some countries.” says Martin Bullemer, Business Development Manager Medical at EOS.
A further stage in the process has been digitized with optical impressions. In the future, more and more dental technicians will thus pick up a computer mouse instead of a wax knife and use an intraoral scanner instead of an impression tray – this saves time and makes work processes more efficient.
Digital manufacturing of dental crowns and bridges
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) has been available to produce crowns and bridges since 2005. Manufacturing systems as well as materials have well established themselves in the dental market. With over 60 installed systems worldwide, it is the most widespread solution on the market. Around 6.8 million units are currently being produced with these systems every year.
The CE-certified material EOS CobaltChrome SP2 (CE 0537) and the EOSINT M 270 system are used for the digital production of crowns and bridges. Both elements of the process chain come from EOS and satisfy the high quality standards for medical products. The finished products comply with the relevant standards EN 1641 as well as EN ISO 22674.
With the EOS systems up to 450 dental crowns and bridges can be cost-efficiently manufactured in 24 hours. This corresponds to an average building time of around three minutes per unit. The final product is characterized by a homogeneous metallic structure with high precision and constant tolerances, enabling a good fitting and reproducible properties. Following the manufacturing process, the dental prosthesis only has to be separated from the platform and a dental technician subsequently further finishes it. The DMLS system can run up to two production cycles per day and can manufacture up to 80,000 units per year. Hardly any personnel are needed to operate the DMLS system except for loading and unloading the system. The AM of dental prostheses is an industrial production process and, thanks to the high productivity of the system, the production costs decrease whiles the quality of the final products remains consistently high. As for the manufacturing of dental restorations 3D data are already available, custom-fit dental models can be produced on the plastic laser-sintering systems FORMIGA P 110 which then serve as the basis for the further processing and veneering of the restorations by the dental technician.
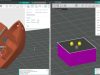
The Digital Manufacturing of Dental Models: economic process, high manufacturing capacity
The FORMIGA P 110 and the material PA 2105 are used to produce dental models. 40 to 70 complete jaw models can be manufactured within 14 hours (excluding cooling time) depending on the design, size and part height. The high production capacity is a result of the multiple layer manufacturing. The individual parts are not connected by support elements, they are only fixed by the surrounding, non-fused powder. On account of the support-free method of production, no manual finishing is necessary, apart from a brief blasting. Automatically, the dental models can be tagged with patient or customer names. Thanks to the mechanical mode of production, the component precision, fit, feel and look are exactly reproducible. Dental models can be directly manufactured a number of times – e.g. as a control model – and in contrast to plaster models are break-proof. Through the time-efficient and economic AM production method, the dental model is ideally produced parallel to the corresponding crown or bridge. The manufacturing time can be reduced on an average by one working day and the dispatch times for conventional impressions can be eliminated fully from the manufacturing chain.
Design and use of the physical model
The EOS technology offers absolute flexibility of design. Within the scope of dimensional accuracy requirements, the dental models can be manufactured as solid or hollow bodies with respective implications for production time and material costs. Common saw-cut models can also be produced and models can be integrated in numerous articular systems as well as model base systems. The models are opaque, match the color of the very popular super-hard plaster and their surface is slightly rough. The properties are therefore comparable to those of the classic master model. What’s more, the plastic models are very hard-wearing, and during steam blasting inherently stable.
The plastic model is primarily used for ceramic veneers, to check for occlusions and to adjust the interproximal contact points. The fit of the crown margin is ensured by the CAD/CAM procedures and should only undergo a visual check. Anatomic impressions for analysis, on the other hand, can be produced and, on account of the temperature resistance, the model is also suitable for the production of aligners.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
3DPResso is a weekly newsletter that links to the most exciting global stories from the 3D printing and additive manufacturing industry.