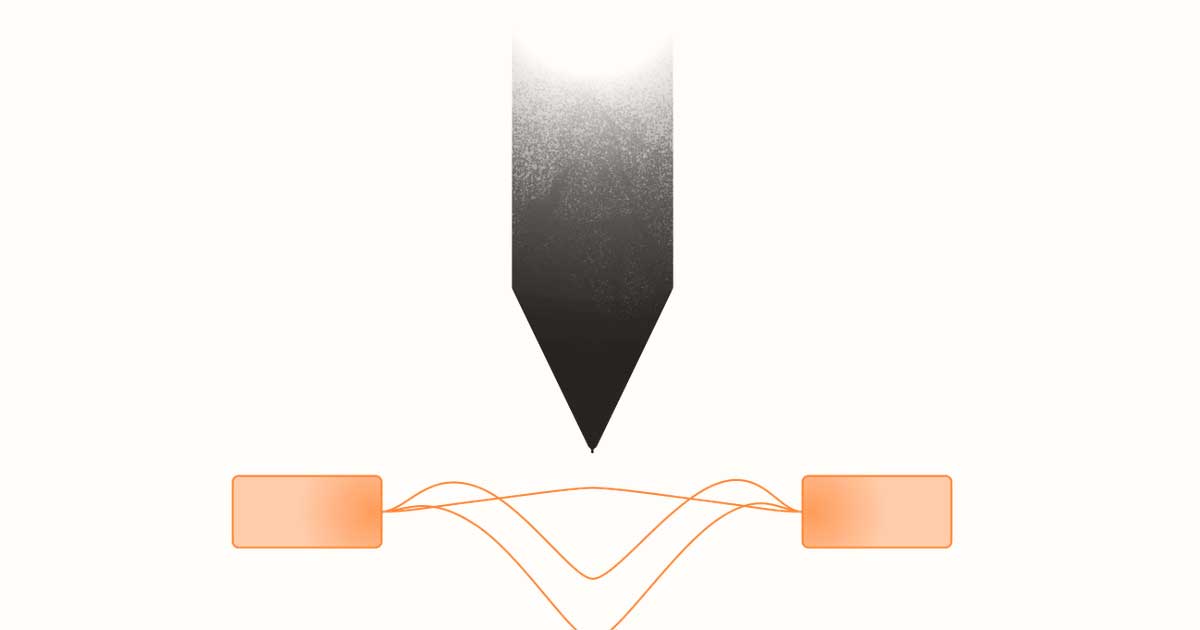
Scrona AG, a 3D printing startup, and Avantama, a provider of high-tech materials for electronics, announced that they have successfully processed high-performance quantum dot (QD) ink using Scrona’s electrohydrodynamic (EHD) inkjet printing process.
The use of Scrona’s electrohydrodynamic (EHD) inkjet printing technology makes it possible to combine the advantages of inkjet printing with high patterning resolution. This promises to enable a new generation of efficient and cost-effective MicroLED displays that simultaneously provide increased color purity and brightness while improving overall production time per pixel.
“We continue to find new applications of EHD that will meet the demands of the industry by offering an additive, completely waste-free process with higher resolution capabilities than lithography patterning,” said Dr. Patrick Galliker, co-founder and CEO of Scrona. “While conventional inkjet printheads require inks of low viscosity, Scona has already demonstrated printing inks 1,000 times what they can process, paving the way for a much more efficient generation of MicroLED displays.”
The Scrona print head technology processes QD inks using EHD inkjet printing. In this process, droplets are ejected from a nozzle by electrostatic forces. By applying an electric field to the outside of the nozzle, ions are attracted to the liquid surface, where they generate mechanical stress. The density of the ions on the surface can be controlled by adjusting the intensity of the voltage used to generate the electric field. The forces generated inside the liquid are not evenly distributed over the surface, as is the case with conventional inkjet printheads, but are concentrated in the center of the nozzle as the liquid is continuously drawn out. The droplet size can be controlled by the applied stresses, including droplets that are an order of magnitude smaller than the nozzle itself.
“Conventional inkjet printing is not a viable option for emerging MicroLED displays because they use much smaller pixels than QD-OLED displays,” said Dr. Norman Lüchinger, co-founder and CTO at Avantama. “By partnering with Scrona, we have been able to demonstrate that an OD greater than 1 can be obtained with a perovskite QD layer thickness below 2µm. This can reduce the printhead nozzle count by a factor of five and deliver a thin QD layer that improves the overall efficiency and production tact time of MicroLED display technology.”
Avantama’s perovskite QDs have the highest absorption coefficients among QDs, enabling the printing of thinner pixels with good optical density and significantly reducing cycle time. Perovskite QDs have the highest weight-based absorption compared to other QDs, which directly translates into very high OD/thickness values. One of the main reasons for this outstanding property is the inherently defect-tolerant nature of perovskites, which means that no passivating cladding is required to enable high emission quantum yields.
This partnership between Scrona and Avantama represents an important step in the advancement of MicroLED display technology and promises to significantly increase efficiency and cost-effectiveness in this area.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
3DPresso is a weekly newsletter that links to the most exciting global stories from the 3D printing and additive manufacturing industry.