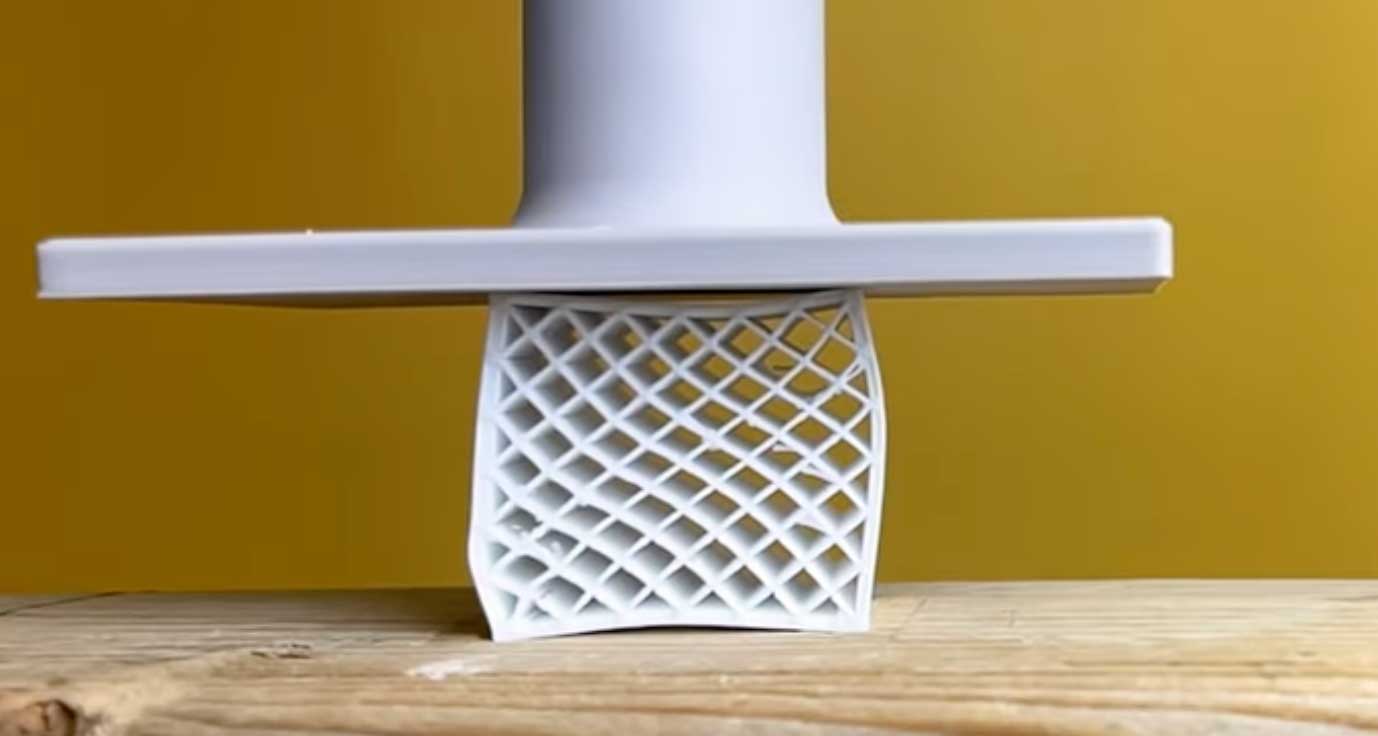
In a YouTube video, the Slant 3D channel tested the most common 3D printing materials for their compression stability. The results were sometimes surprising in terms of the maximum load-bearing capacity that the tested materials could withstand.
Five materials were tested: PLA, PETG, ABS, TPU and PA6 nylon. These were printed in the form of cuboids with identical dimensions and then compressed with increasing force. The maximum load before the sample broke was measured in each case.
Contrary to expectations, PLA withstood the greatest force. Although the plastic is considered to be brittle and fragile, the sample withstood a load of approx. 530 lbf (2362 Newtons) through uniformly increasing compression. Only then did a brittle fracture occur.
According to the video makers, the high rigidity of the material is the reason for this unexpectedly good result. PLA is therefore ideal for printed parts that are exposed to high pressure loads.
Nylon, on the other hand, performed surprisingly poorly. The material, which is actually known for its high tensile and impact strength, only withstood 189 lbf (844 newtons) of stress before the structure gave way. According to the testers, this was due to the great flexibility of the material, which was unable to offer sufficient resistance to the pressure.
TPU proved to be many times more elastic, deforming considerably under pressure without breaking. The side walls only collapsed at the force limit of the test setup. PETG (485 lbf / 2160 Newton) and ABS (472 lbf / 2100 Newton) were in the middle of the field.
The complete test can be viewed here:
Subscribe to our Newsletter
3DPresso is a weekly newsletter that links to the most exciting global stories from the 3D printing and additive manufacturing industry.