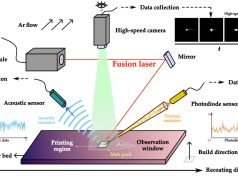
The Institute of Power Engineering (IEn) in Poland has set a milestone with the HYDROGIN system: a system with stacks of solid oxide electrochemical cells manufactured by cost-efficient techniques, including 3D printing. This system was supplied to CBRF Energa S.A., ORLEN and, through its integration with Energa’s cogeneration plant in Elblag, improves its operational flexibility and increases the use of renewable energy for hydrogen production.
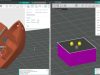
The ceramic seals for the HYDROGIN electrochemical cells were manufactured using 3D printing processes, using machines from Sygnis S.A., a Polish research and development company.
Of particular note is the rSOC technology, which outshines other types of electrolytes with its remarkable hydrogen generation efficiency (>92%).
“The installation is a small-scale demonstration of a first-of-a-kind system with stacks of solid oxide electrochemical cells which can operate interchangeably in electrolysis or fuel cell mode. The pilot plant which is thermally and electrically integrated with a CHP station proves that conventional power generation assets can play a new role as sources of steam and energy for large-scale hydrogen production. The replicability of this solution is extremely broad and can be successfully used in hydrogen generation for various industries and for energy storage. We are proud that the first in the world system of this type has been built based on our technology was constructed by the Institute of Power Engineering”, says Professor Jakub Kupecki, Director of the Institute of Power Engineering, and Director of the Center for Hydrogen Technologies (CTH2 IEn) in an interview with Energa S.A. – ORLEN.
Another highlight: The seals developed at the Institute of Energy Technology were created using a novel 3D printing method with ceramic paste. This method allows sealing material with the right rheological properties to be applied directly to the flat and corrugated surfaces of rSOC stack elements.
Sygnis S.A. has developed and produced machines for this special application.
“We are very pleased to see that the machines we made on request for the Institute of Power Engineering, which we implemented consecutively within the last year, are now performing well. We congratulate Prof. Jakub Kupecki, Dr. Marek Skrzypkiewicz, Dr. Agnieszka Żurawska, and Ms. Magdalena Kosiorek and the team of CTH2 IEn for their great ideas, hard work and achievements. We are confident that Sygnis S.A.’s existing and upcoming technology solutions will accelerate the work of hundreds of other research groups around the world”, says Andrzej Burgs, CEO of Sygnis SA.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
3DPResso is a weekly newsletter that links to the most exciting global stories from the 3D printing and additive manufacturing industry.